NO INCOME TAX ON ANNUAL INCOME UPTO Rs. 12 LAKH UNDER NEW TAX REGIME

1. Revised Tax Slabs
The Income Tax Bill-2025 introduces new tax slabs for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) to provide relief to middle-income groups and stimulate consumption.
Impact: The revised slabs aim to increase disposable income for middle-class taxpayers, encouraging spending and savings.
2. Increased Standard Deduction
LIMIT TO BE Rs. 12.75 LAKH FOR SALARIED TAX PAYERS, WITH STANDARD DEDUCTION OF RS. 75,000.
Impact: This move will reduce the tax burden on salaried employees and pensioners, providing them with more take-home income.
3. Enhanced Deductions for Investments
TAX SLAB RATE REDUCTION AND REBATES TO RESULT IN SUBSTANTIAL TAX RELIEF TO MIDDLE CLASS, THEREBY BOOSTING HOUSEHOLD CONSUMPTION EXPENDITURE AND INVESTMENT.
Impact: This is expected to encourage long-term savings and investments in sustainable and innovative sectors.
Reaffirming Government’s commitment to the philosophy of “trust first, scrutinize later”, the Union Budget 2025-26 has reposed faith in the Middle class and continued the trend of giving relief in tax burden to the common tax–payer. Presenting the Budget in the Parliament today, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman proposed an across-the-board change in tax slabs and rates to benefit all tax-payers.

Giving the good news to tax payers, the Finance Minister stated, “There will be no income tax payable upto income of Rs. 12 lakh (i.e. average income of Rs.1 lakh per month other than special rate income such as capital gains) under the new regime. This limit will be Rs.12.75 lakh for salaried tax payers, due to standard deduction of Rs. 75,000.” Tax rebate is being provided in addition to the benefit due to slab rate reduction in such a manner that there is no tax payable by them, she added.
Smt. Sitharaman stated, “The new structure will substantially reduce the taxes of the middle class and leave more money in their hands, boosting household consumption, savings and investment”. In the new tax regime, the Finance Minister proposed to revise tax rate structure as follows:
| 0-4 lakh rupees | Nil |
| 4-8 lakh rupees | 5 per cent |
| 8-12 lakh rupees | 10 per cent |
| 12-16 lakh rupees | 15 per cent |
| 16-20 lakh rupees | 20 per cent |
| 20- 24 lakh rupees | 25 per cent |
| Above 24 lakh rupees | 30 per cent |
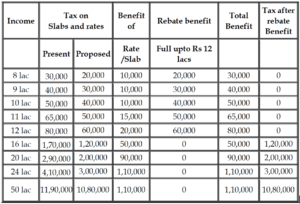
The total tax benefit of slab rate changes and rebate at different income levels can be illustrated in the table Above.
4. Tax Incentives for Startups
To promote entrepreneurship, the bill extends the tax holiday for startups by an additional two years. Startups will also benefit from a reduced corporate tax rate of 15% for the first five years of operation.
Impact: This will foster innovation, job creation, and economic growth by supporting new businesses.
5. Digital Economy and Cryptocurrency Taxation
The bill introduces a new tax framework for digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and NFTs. A flat tax rate of 30% will apply to gains from the sale of digital assets, with no deductions allowed.
Impact: This move aims to bring clarity and regulation to the burgeoning digital asset market while ensuring tax compliance.
6. Measures to Curb Tax Evasion
The bill includes stringent measures to combat tax evasion, such as:
- Mandatory linking of PAN with Aadhaar for all taxpayers.
- Introduction of a new anti-evasion portal for real-time monitoring of high-value transactions.
- Higher penalties for non-compliance and concealment of income.
Impact: These measures are expected to improve tax compliance and increase government revenue.
7. Corporate Tax Reforms
The bill proposes a reduction in the corporate tax rate for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) from 25% to 22%. Large corporations will continue to enjoy the existing rate of 22% (with surcharge and cess).
Impact: This will boost the competitiveness of SMEs and support their growth.
8. Green Tax Incentives
To promote environmental sustainability, the bill introduces tax benefits for investments in renewable energy projects, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient appliances.
Impact: This aligns with India’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 and encourages eco-friendly practices.
9. Simplification of Tax Filing Process
The bill introduces a simplified, single-page tax return form for individuals with income up to ₹10 lakh. Additionally, pre-filled tax forms will be made available to reduce errors and save time.
Impact: This will make tax filing more user-friendly and reduce the compliance burden on taxpayers.
10. Special Provisions for Senior Citizens
The bill increases the tax exemption limit for senior citizens from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh. Additionally, the interest income limit for tax-free savings accounts (under Section 80TTB) has been raised from ₹50,000 to ₹1 lakh.
Impact: This will provide financial relief to senior citizens and improve their quality of life.
11. Introduction of Wealth Tax
The bill reintroduces a wealth tax on individuals with a net worth exceeding ₹50 crore. The tax rate will be 1% on wealth above this threshold.
Impact: This aims to address income inequality and generate additional revenue for social welfare programs.
12. Implementation Timeline
The Income Tax Bill-2025 is expected to be passed in the upcoming parliamentary session and will come into effect from April 1, 2025, for the financial year 2025-26.
While underlining Taxation Reforms as one of key reforms to realize the vision of Viksit Bharat, Smt. Sitharaman stated that the new income-tax bill will carry forward the spirit of ‘Nyaya’. The new regime will be simple to understand for taxpayers and tax administration, leading to tax certainty and reduced litigation, she informed.
Quoting Verse 542 from The Thirukkural, the Finance Minister stated, “Just as living beings live expecting rains, Citizens live expecting good governance.” Reforms are a means to achieve good governance for the people and economy. Providing good governance primarily involves being responsive. The tax proposals detail just how the Government under the guidance of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has taken steps to understand and address the needs voiced by our citizens, Smt. Sitharaman added.
Disclaimer: The details provided in this blog are based on the proposed Income Tax Bill-2025 and are subject to change based on parliamentary discussions and approvals. Readers are advised to consult a tax professional for personalized advice.



